Category: Etching

Product Details:
| CAS No | 7727-54-0 |
| Grade Standard | Industrial Grade |
| Physical State | Powder |
| Usage/Application | Utilized as a strong oxidizing agent in industries such as electronics, textiles, and cosmetics for processes like etching, bleaching, and polymerization. |
| HS Code | 28334000 |
| Packaging Details | 200 litres Drum |
| Chemical Formula | ?(NH?)?S?O? |
| Purity % | >99% |
| Country of Origin | Made in India |
Ammonium Persulfate Overview:
Ammonium persulfate (APS), with the chemical formula (NH4)2S2O8, is a white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. It is a strong oxidizing agent and is commonly used in various industrial processes, laboratory applications, and as an initiator in polymerization reactions.
Key Characteristics:
- White, crystalline solid
- Highly soluble in water
- Strong oxidizing agent
Applications:
- Polymerization Initiator: Ammonium persulfate is widely used as an initiator in the polymerization of acrylics, vinyl acetate, and other monomers to produce plastics, adhesives, and coatings.
- Oxidative Etching: It is employed in printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing as an etchant to remove copper from circuit boards.
- Hair Bleaching: Ammonium persulfate is used in hair bleaching formulations as an oxidizing agent to lighten hair color.
- Chemical Synthesis: It serves as a source of sulfate radicals in various chemical reactions, including the synthesis of organic compounds and the oxidative degradation of pollutants.
- Laboratory Reagent: Ammonium persulfate is used in laboratories as a reagent for protein purification, DNA extraction, and as an oxidizing agent in chemical analysis.
Hazards:
- Irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
- Inhalation of dust may cause respiratory irritation and coughing.
- Ingestion may lead to gastrointestinal irritation, nausea, and vomiting.
- Strong oxidizing properties may cause spontaneous combustion when in contact with combustible materials.
Product Enquiry

Product Details:
| CAS No | 1310-73-2 |
| Grade Standard | Industrial Grade |
| Physical State | Solid |
| Usage/Application | Essential in industries for its role in chemical manufacturing, water treatment, and as a strong base in various processes including soap and paper production. |
| HS Code | 281511 |
| Packaging Details | ?25 / 50 kg HDPE bags with inner HM-HDPE liner |
| Chemical Formula | ?NaOH |
| Purity % | >99% |
| Country of Origin | Made in India |
Sodium Hydroxide Overview:
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), commonly known as caustic soda or lye, is a highly caustic and reactive inorganic compound. It is a white, deliquescent solid at room temperature and is soluble in water. Sodium hydroxide is widely used in various industrial processes, laboratory applications, and as a cleaning and disinfecting agent.
Key Characteristics:
- White, deliquescent solid
- Highly soluble in water
- Strongly alkaline with a slippery feel
Applications:
- Chemical Manufacturing: Sodium hydroxide is a key ingredient in the production of various chemicals, including soaps, detergents, textiles, and paper.
- Petroleum Refining: It is used in petroleum refining processes for the neutralization of acidic impurities and the saponification of fats and oils.
- Water Treatment: Sodium hydroxide is employed in water treatment plants for pH adjustment, neutralization of acidic water, and removal of heavy metals.
- Aluminum Production: It is used in the production of aluminum metal through the Bayer process, where it is used to dissolve aluminum oxide from bauxite ore.
- Cleaning and Degreasing: Sodium hydroxide is used as a cleaning and degreasing agent in household cleaners, industrial degreasers, and oven cleaners.
Hazards:
-
- Highly corrosive to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
- Inhalation of vapors or dust may cause severe respiratory irritation.
- Contact with water releases heat and may cause burns or splattering.
- Reacts violently with acids, metals, and organic materials, posing fire and explosion risks.
Product Enquiry
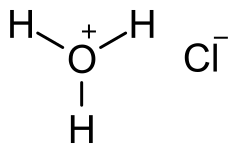
Product Details:
| CAS No | 7647-01-0 |
| Grade Standard | Industrial Grade |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Usage/Application | Essential in various industries for processes such as chemical synthesis, metal cleaning, and pH adjustment in water treatment. |
| HS Code | 28111100 |
| Packaging Details | 200 litres Drum |
| Chemical Formula | HCl |
| Purity % | >30% |
| Country of Origin | Made in India |
?
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) Overview:
Hydrochloric acid, often abbreviated as HCl, is a strong mineral acid with a pungent, sharp odor. It is colorless when pure and is highly corrosive in its concentrated form. Hydrochloric acid is widely used in various industrial processes, laboratory applications, and as a chemical reagent.
Key Characteristics:
- Strong mineral acid
- Colorless liquid with a pungent odor
- Highly corrosive and reactive
Applications:
- Industrial Processes: Hydrochloric acid is utilized in numerous industrial processes, including steel pickling, metal cleaning, ore processing, and chemical synthesis.
- Laboratory Reagent: It serves as a versatile reagent in chemical laboratories for various applications, such as pH adjustment, titration, and chemical analysis.
- Food Industry: Hydrochloric acid is used in the food industry for pH control, water treatment, and as an acidifier in food processing.
- Water Treatment: It is employed in water treatment plants to adjust pH levels and remove impurities from water supplies.
- Pharmaceuticals: Hydrochloric acid is used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, including drug synthesis and as an excipient in tablet formulations.
Hazards:
- Highly corrosive and can cause severe burns upon contact with skin, eyes, or mucous membranes.
- Inhalation of vapors may cause irritation to the respiratory system and damage to lung tissue.
- Ingestion of concentrated solutions can lead to severe gastrointestinal injury and internal corrosion.
- Proper handling and storage precautions are necessary due to its hazardous nature.
[/read]
Product Enquiry
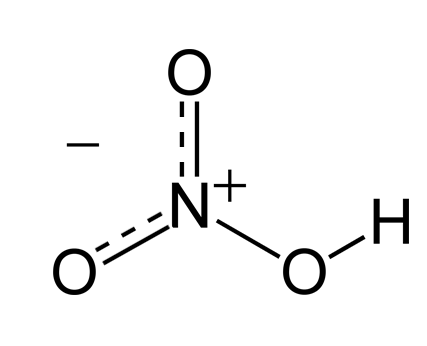
Product Details:
| CAS No | 7697-37-2 |
| Grade Standard | Industrial Grade |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Usage/Application | Employed in various industries for metal processing, fertilizer production, and as a precursor in chemical synthesis. |
| HS Code | 28080010 |
| Packaging Details | 200 litres Drum |
| Chemical Formula | HNO? |
| Purity % | >70% |
| Country of Origin | Made in India |
Nitric Acid (HNO3) Overview:
Nitric acid is a highly corrosive mineral acid with the chemical formula HNO3. It is colorless when pure and is known for its strong oxidizing properties. Nitric acid plays a vital role in various industrial processes, laboratory applications, and as a reagent in chemical synthesis.
Key Characteristics:
- Highly corrosive mineral acid
- Colorless liquid with a sharp odor
- Strong oxidizing agent
Applications:
- Metal Etching: Nitric acid is used for etching and cleaning metals, such as stainless steel and aluminum, in various industrial processes.
- Fertilizer Production: It is a key ingredient in the production of ammonium nitrate, a widely used fertilizer.
- Explosives Manufacturing: Nitric acid is utilized in the production of explosives, such as TNT (trinitrotoluene) and nitroglycerin.
- Laboratory Reagent: It serves as a reagent in chemical analysis, organic synthesis, and as a nitrating agent.
- Pickling Agent: Nitric acid is used for pickling metals to remove scale, rust, and other impurities.
Hazards:
- Highly corrosive and strong oxidizing agent.
- Can cause severe burns upon contact with skin, eyes, or mucous membranes.
- Inhalation of vapors may lead to respiratory irritation, coughing, and lung damage.
- Exposure to nitric acid fumes may result in pulmonary edema and systemic toxicity.
Product Enquiry

Product Details:
| CAS No | 7664-93-9 |
| Grade Standard | Industrial Grade |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Usage/Application | Widely used in industries for chemical synthesis, metal processing, and as an electrolyte in lead-acid batteries. |
| HS Code | 28070010 |
| Packaging Details | 200 litres Drum |
| Chemical Formula | H?SO? |
| Purity % | >95% |
| Country of Origin | Made in India |
?
Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) Overview:
Sulfuric acid, with the chemical formula H2SO4, is a strong mineral acid known for its corrosive properties and diverse industrial applications. It is colorless to slightly yellow in its pure form and is commonly used in manufacturing, chemical synthesis, and laboratory procedures.
Key Characteristics:
- Strong mineral acid
- Colorless to slightly yellow liquid
- Highly corrosive and reactive
Applications:
- Chemical Manufacturing: Sulfuric acid is a key component in the production of various chemicals, including fertilizers, explosives, detergents, and pharmaceuticals.
- Petroleum Refining: It is used in petroleum refining processes for the purification of petroleum products and as a catalyst in alkylation reactions.
- Battery Manufacturing: Sulfuric acid is used in lead-acid batteries as an electrolyte to facilitate energy storage and discharge.
- Metal Processing: It is employed in metal processing industries for pickling, electroplating, and metal surface treatment.
- Water Treatment: Sulfuric acid is used in water treatment plants for pH adjustment, wastewater treatment, and the removal of heavy metals.
Hazards:
- Highly corrosive and can cause severe burns upon contact with skin, eyes, or mucous membranes.
- Inhalation of vapors may cause irritation to the respiratory system and damage to lung tissue.
- Ingestion of concentrated solutions can lead to severe gastrointestinal injury and internal corrosion.
- Sulfuric acid can react violently with water and other substances, posing fire and explosion risks.
[/read]
